| Linha 18: | Linha 18: | ||
** Quarters after 4G launch | ** Quarters after 4G launch | ||
*** Source GSMA | *** Source GSMA | ||
* 4G-LTE Adoption 2017-1 | |||
[[Arquivo:4G-Adoption.jpg]] | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Edição das 19h31min de 12 de maio de 2017
Updates do 5G
Small Overview
What is 5G
- 2G - 1990 - Mobile voice & SMS
- 3G
- 4G
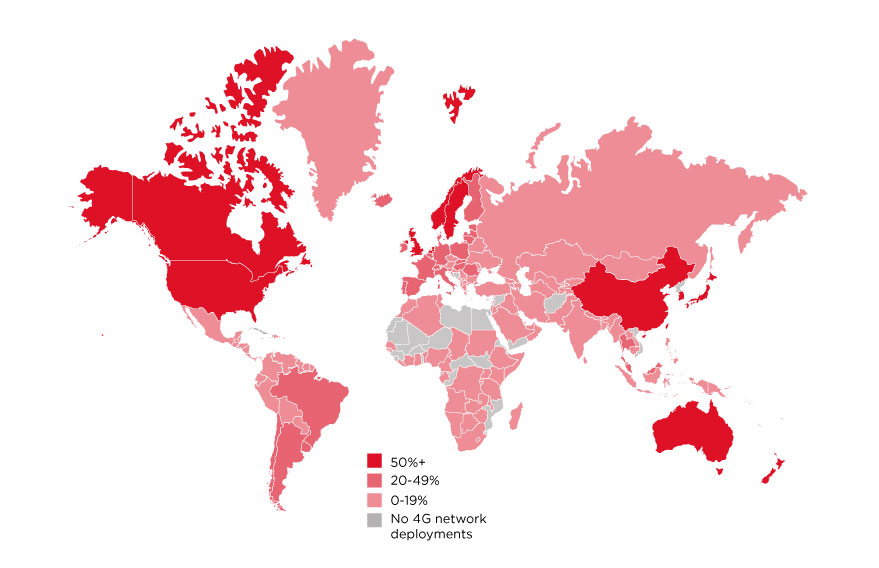
4G deployment globally
- 4G connections (% of total connections, normalized)
- 4G population coverage
- Quarters after 4G launch
- Source GSMA
- Quarters after 4G launch
- 4G-LTE Adoption 2017-1
5G is integrating verticals
- 2G
- 3G
- 4G
- 5G - 2020 Every vertical connected
- 5G needs to incorporate different characteristics and requirements of the vertcials
- Ratio of uplink to downlink in Bytes x propagation
- 5G empowering verticals
- Factors of the future
- IoT
- narrow cells
- Energy
- Smart grid
- eHealth
- Automtive
- Media & Entertainment
romper todo o tipo de soluções que não passem pela operadora
Evolutions in requirements
- Vertical have diverse requirements
- eHealth
- Assets and interventions management in Hospital
- Robotics
- REmote monitoring
- Smarter medication
- eHealth
- Use case categories definition (NGMN)
- Families Categories USe cases
- Broadband access in dense area
- Broadband access everywhere
- High user mobility
- Massive IoT
- User experience requirements (NGMN)
- Use cases category ux data rate
Source 5G White paper Feb 2015
- system performance requirements (NGMN)
Enhancement of key capabilities from IMT-Advanced to IMT-202 ITU-R
- ITU-R- IMT Vision - Frameworkss and overall objectives of the future developments of IMT for 2020 and beyond recommendation
Phases and expecteed timelines for IMT-2020 (ITU-R)
- ITU-R- IMT Vision - Frameworkss and overall objectives of the future developments of IMT for 2020 and beyond recommendation
Gráfico 2000 - 2014 - ---------2019 - 2020
- WRC => Tudo é definido por ele
Ongoing technology trends NGMN
- A Network capabilities
- B Enablers for operational sustain
- C Enablers for business agility
- Current trends
- SON NFV SDN FMC API exposure offloading(D2D, WiFi .. Multi-RAt Convergence
- CA Carrier agreagation Dual connectivity MIMO/CoMp
- License-assisted access Traffic Optimization (DPI, caching, rate adaptation)
- Network densification Security (HTTPS) Content Optimization (DASH)
- VAS (big data, AAA, billing, etc)
- Current trends
5G design principles
- Radio
- Leverage spectrum
- Enable cost-effective dense deployments
- Coordinate and cancel interference
- Support dynamic radio topology
- Network
- Create common composabel core
- Operations & Management
- Simplify operation and management
Cross:
Embrace flexible functionn and capabilities
Support new value creation
Build in security and privacy
5G network slices implemented on the same infra NGMN
- 5G slice 1 - smartphones
- 5G slice 1 - autonomous driving
- 5G slice 1 - massive IoT
- other slices
NGMN 5G WP
Access technology interfacing options NGMN
- Option 1: EPC - Fixed NW - Fixed-Wi-Fi - New RAT - 4G evolution
- Option 2: EPC - 5G NW functions - Fixed NW - Fixed-Wi-Fi - New RAT - 4G evolution
- Option 3: EPC - 5G NW functions - Fixed NW - Fixed-Wi-Fi - New RAT - 4G evolution
Pros Cons
Key topics for 5G architecture Desing
passou rápido
RAN - CN Split
Logical split between RAN and CN allows for independent evolution of obth RAN and CN and cross layer optimizations in some deployments whrn the functions are co-located Flexible assignment and integration of RAN and CN functions to provide a high degree ...
Physical Archit of a FMC network
Source: 5G PPP archtecture working group
Network softwarisation & programmability
5G PPP Archit Working Group
Service centric network Function Virtualization and deployment
Service centric - Service layer - Software network service chain layer - Networking slice layer - Resource abstraction and virtualisation layer
Evolutions in technologies
Enhanced mobile diferent scenarios 5G PPP Automotive Vission Oct 20 2015
SAE/VDA automation levels
- Levels of driving automation acc to SAE and VDA
==